Martin Gilens has done some very interesting work on the way that politicians respond to public opinion, and his key result is that Congress doesn’t really care much about the poor (no surprise) and cares only modestly about the middle class (a bit of a surprise). What they care about are the upper middle class and the rich.
Today he puts up a chart that gives this result a bit more nuance. The blue bars represent middle-income voters, and during election years they have a moderate amount of influence. Not as much as the well-off, but when an election is imminent politicians pay at least some attention to the preferences of the middle class (and, to a smaller extent, the poor).
So when do the rich get their payoff? Answer: during non-election years, when no one is paying attention. In those years, members of Congress respond solely to the 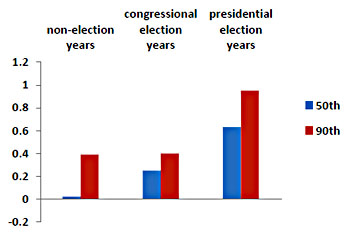 preferences of the well-off. What’s more, laws passed during non-election years are more durable:
preferences of the well-off. What’s more, laws passed during non-election years are more durable:
The hopeful side of this observation is that democratic institutions do work, to an extent, to discipline policymakers and bring policy outcomes more in line with the public’s desires. But these periods of heightened responsiveness are the exception, not the rule, and it appears that policies “forced” on decision makers by political circumstances fare less well over time than those adopted under less “coercive” conditions. Although policies adopted during presidential election years are more consistent with public preferences, they are also more likely to lose funding over time than are policies adopted in other years of the quadrennial election cycle.
To summarize: In election years we throw a few sops to the 90%. During non-election years, we cut back the funding for those sops and pass the legislation that the top 10% want passed. Welcome to America.