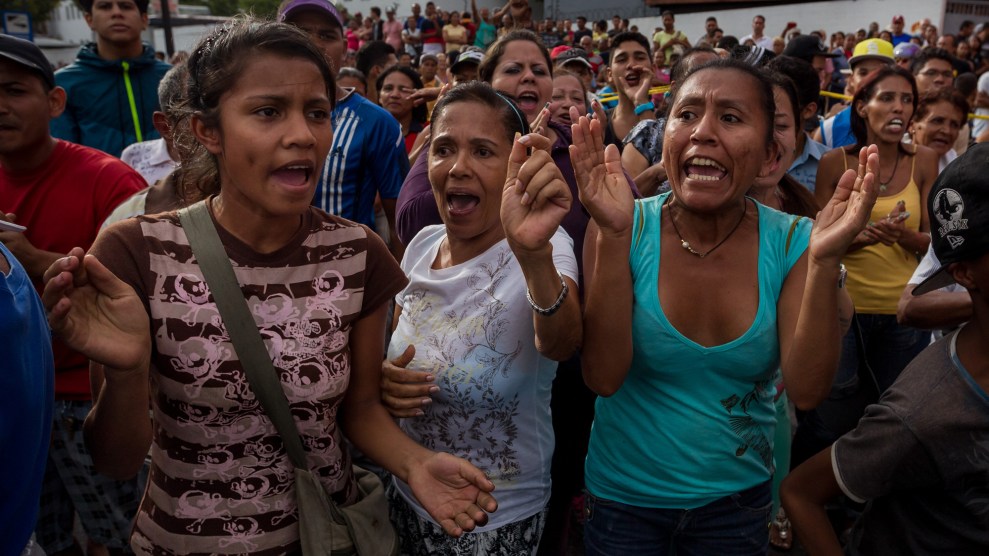
People line up to buy food in Caracas.<a href="http://www.zumapress.com/zpdwnld/20160615_zaf_e26_023.jpg?type=hires">Miguel Gutierrez</a>/EFE via ZUMA Press
Earlier this year, Venezuelan journalist and political scientist Francisco Toro described his home country as “the world’s most visibly failing state.” And now, amid a worsening economic crisis, a crackdown on political opposition, and increasing violent crime, more and more of his countrymen are seeking haven in the United States.
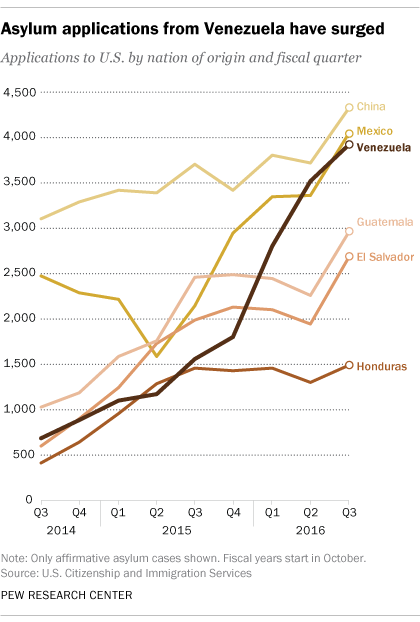
Over the past year, the United States has experienced a surge in asylum applications from Venezuela, according to new data from the Pew Research Center. So far in fiscal 2016, applications from Venezuela soared past 10,000, an increase of 168 percent compared with the fiscal year 2015.
Venezuela’s economic collapse has been making headlines for more than a year. Oil prices plummeted, and price controls led to shortages of basic staples like food and medicine. A recent study from Simón Bolívar University found that 9 out of 10 Venezuelans can no longer afford to buy enough food. Now, people wait in line for hours for essentials like rice and cooking oil, sometimes even fending off armed thieves. As food riots became a daily occurrence, President Nicolás Maduro—who succeeded Hugo Chávez after his death in 2013—put the army in charge of rationing. Food is now transported by armed guards, and police protect against looters. The International Monetary Fund has estimated that Venezuela’s inflation rate will reach 480 percent this year, and more than 1,600 percent next year. Unemployment is around 17 percent and is expected to grow to a quarter over the next three years.
On top of all that, Maduro has been cracking down on his political opponents. In December, the opposition coalition won a major victory, securing a majority of seats in parliament for the first time since Chávez came to power in 1999. After that, Maduro intensified his crackdown. The Venezuelan Penal Forum, which tracks human rights abuses, counted 96 political prisoners in June, compared with just 11 when Maduro became president. Meanwhile, election officials signaled earlier this week that a long-promised recall election to oust Maduro would have to wait until 2017.
This combination of food and medicine shortages, political instability, and increasing violent crime is driving Venezuelans out of the country, according to Julio Henriquez, director of the Boston-based nonprofit Refugee Freedom Program, which currently focuses on helping Venezuelan asylum seekers. “There was a lot of hope that the new parliament would make a big difference in the human rights conditions,” he says, “but human rights conditions have worsened.”
So far, Henriquez says, most of the Venezuelan asylum seekers he’s encountered have been middle-class people who’ve come to the United States via a student or tourist visa and then applied for asylum after their arrival. It’s quite a contrast to the Central American families showing up at the US-Mexico border, a situation which advocates have warned for years amounts to a refugee crisis.
Faye Hipsman, an analyst with the Migration Policy Institute, says some Venezuelan asylum applicants may be taking advantage of excessive backlogs in the application process—delays that allow applicants to stay in the United States for years pending the outcome of their claim. And while many are likely fleeing poverty, hunger, and general violence, Hipsman says, it’s often not enough to qualify for asylum, which requires applicants to prove that they risk persecution based on their race, religion, nationality, political opinion, or social group.
“A share of these people have legitimate asylum claims,” she says. “But there’s a lot of concern that for legitimate reasons, people don’t want to go back to Venezuela because it’s dangerous there—and the circumstances are really bad.”