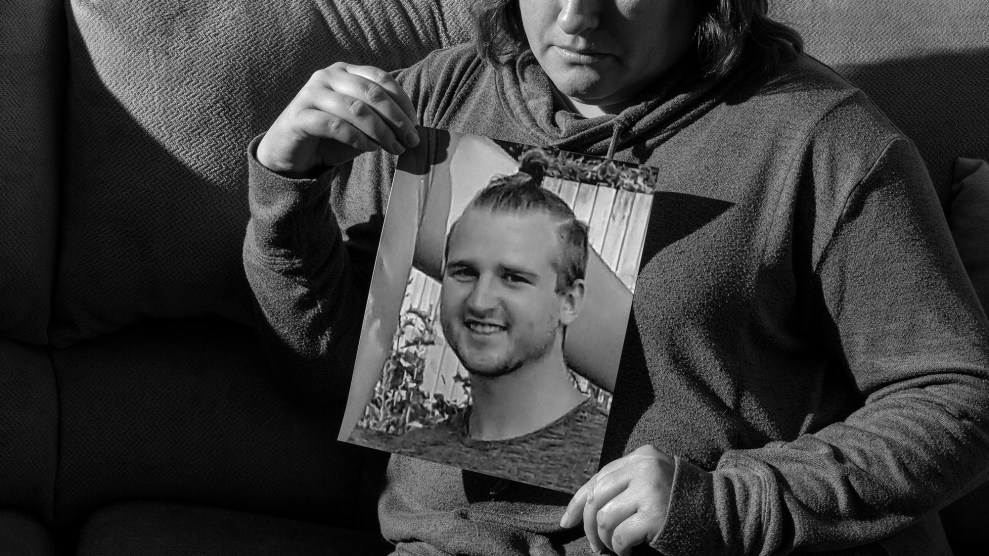
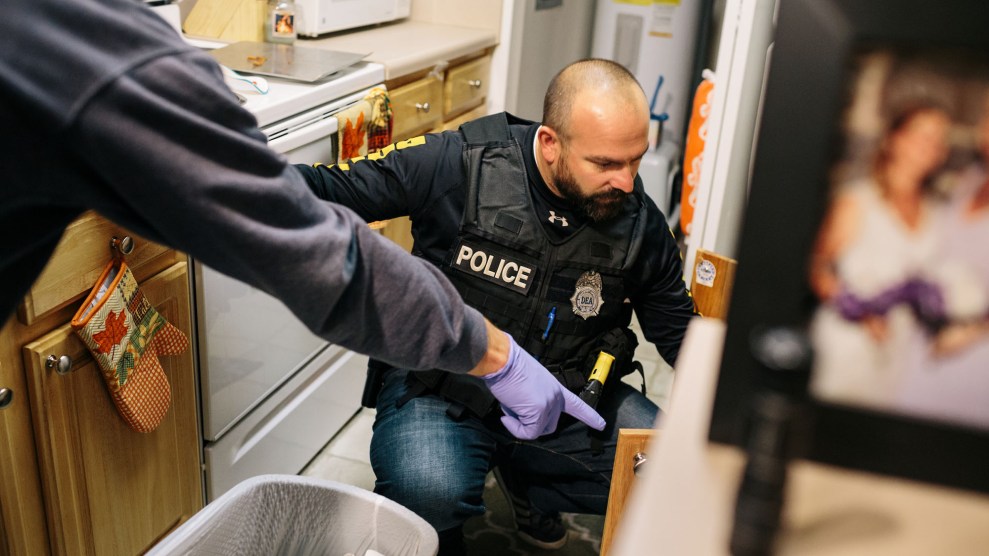
Overdose rates fell in 2018 for the first time in 28 years, according to a new report from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. But the death toll still remains unfathomably high: In 2018, some 67,000 Americans died of overdoses, compared to 70,000 the year before. That makes 2018 the second-deadliest year for drug overdoses in US history, claiming more lives than gun violence or car crashes.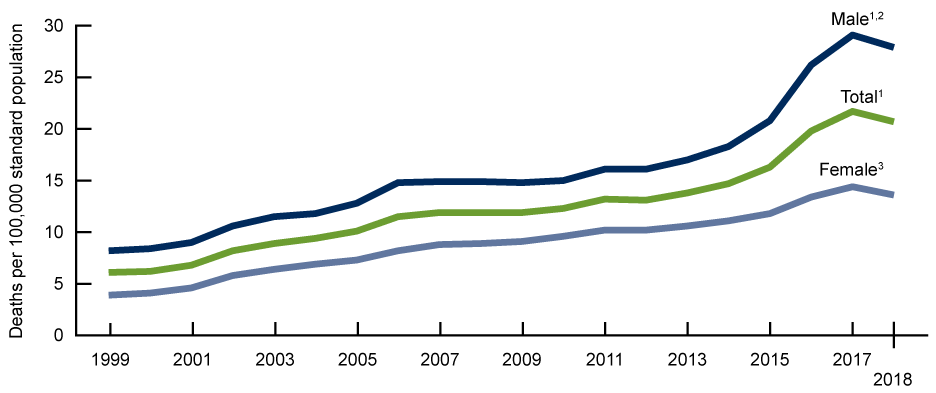
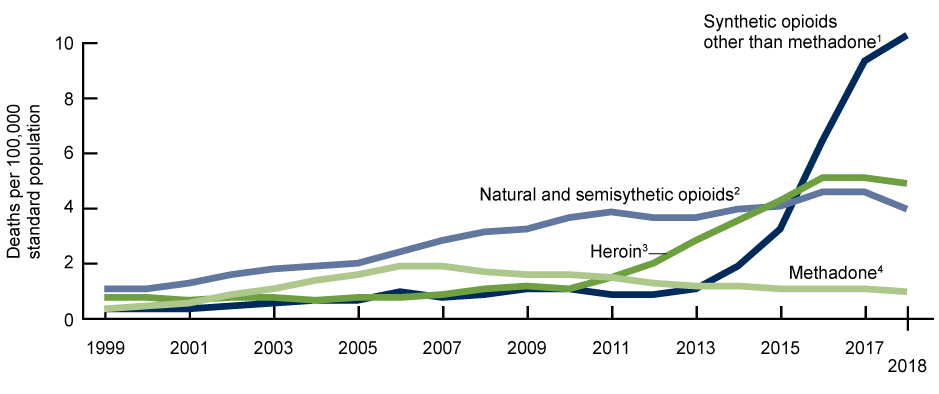
Overdose rates in 2018 decreased significantly in 14 states, including some that have historically been the worst hit by the opioid crisis, like West Virginia, Ohio, and Pennsylvania. Life expectancy, which had declined for the past three years in part due to soaring overdose rates, increased slightly in 2018, to an average of 78.7 years. But drug deaths involving synthetic opioids like fentanyl continued to rise in 2018, as did those involving cocaine and psychostimulants like methamphetamine.
The Trump administration was quick to claim credit for the good news: “This has not happened through coincidence—it’s happened through causation,” said White House advisor Kellyanne Conway in a press briefing on Thursday. James Carroll, the director of the Office of National Drug Control Policy, used the occasion to promote the wall at the Southern border, which “is one of the many tools that we are using to counter drug traffickers,” he said.
Yet experts point to different factors, including the decline in opioid prescription rates since 2012. Though Trump promised to “spend the money” necessary to address the opioid crisis, the administration’s efforts have largely fallen short. Trump’s ongoing attempts to dismantle the Affordable Care Act threaten addiction treatment coverage for millions of Americans. On the same day that Conway touted Trump’s overdose prevention efforts, the White House rolled out plans to to significantly cut Medicaid funding, which provides insurance coverage for one in five low-income Americans.
“This improvement came about in spite of the Trump Administration,” said Stanford drug policy expert Keith Humphreys, noting that Congress has “successfully resisted many of the cuts to Medicaid and to health exchanges that Trump has tried to implement, which would have worsened the epidemic.”